Cows are heifers that were bred by bulls and had a baby calf. Hang up during your.
Field To Fork.
Life cycle of beef cow. The Life Cycle of Beef Cattle Production 1. Beginning Stage Bull Cow Calf 2A. Grass Finished Middle Stage Final Stage.
Here cattle typically spend four to six months during which time they have room to move around and eat at feed bunks containing a carefully-balanced diet made up of roughage such as hay grass and fiber grain such as corn wheat and soybean meal and local renewable feed sources such as the tops of sugar beet plants potato peelings or even citrus pulp. Veterinarians nutritionists and cattlemen work. The beef lifecycle is perhaps one of the most unique and complex lifecycles of any food.
It takes anywhere from 2-3 years to bring beef from farm to fork. The beef community is not vertically integrated meaning that an animal will change owners or caretakers an average of 2-3 times during its lifetime. Each caretaker along the way specializes in a key area of a cows life providing the proper care nutrition.
Cows are heifers that were bred by bulls and had a baby calf. Cows have a 9 month gestation period and typically have a calf every 12 months. All cows spend their entire lives Approx.
7-10 years grazing on grass or forage and mothering baby calves. When they are no longer able to have calves cows are harvested for beef see final stage. Cows will remain active in the breeding herd for about seven years.
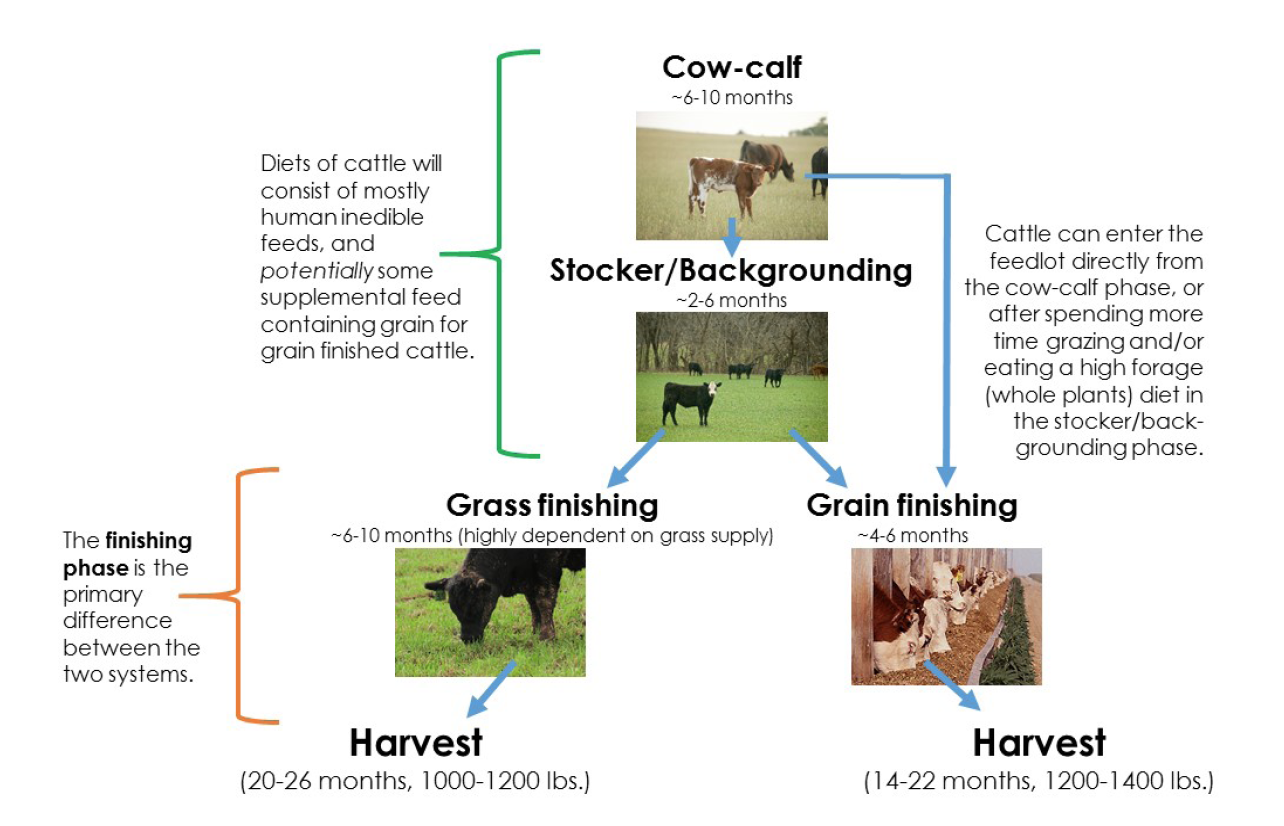
A calf is weaned at six to seven months of age and at a weight of about 227 kg. For the next stage of the beef production cycle the beef animal will typically be brought to a finished market weight of approximately 550 to 700 kg in specialized feedlots. Visit the virtual beef feedlot tour to learn more about this aspect.
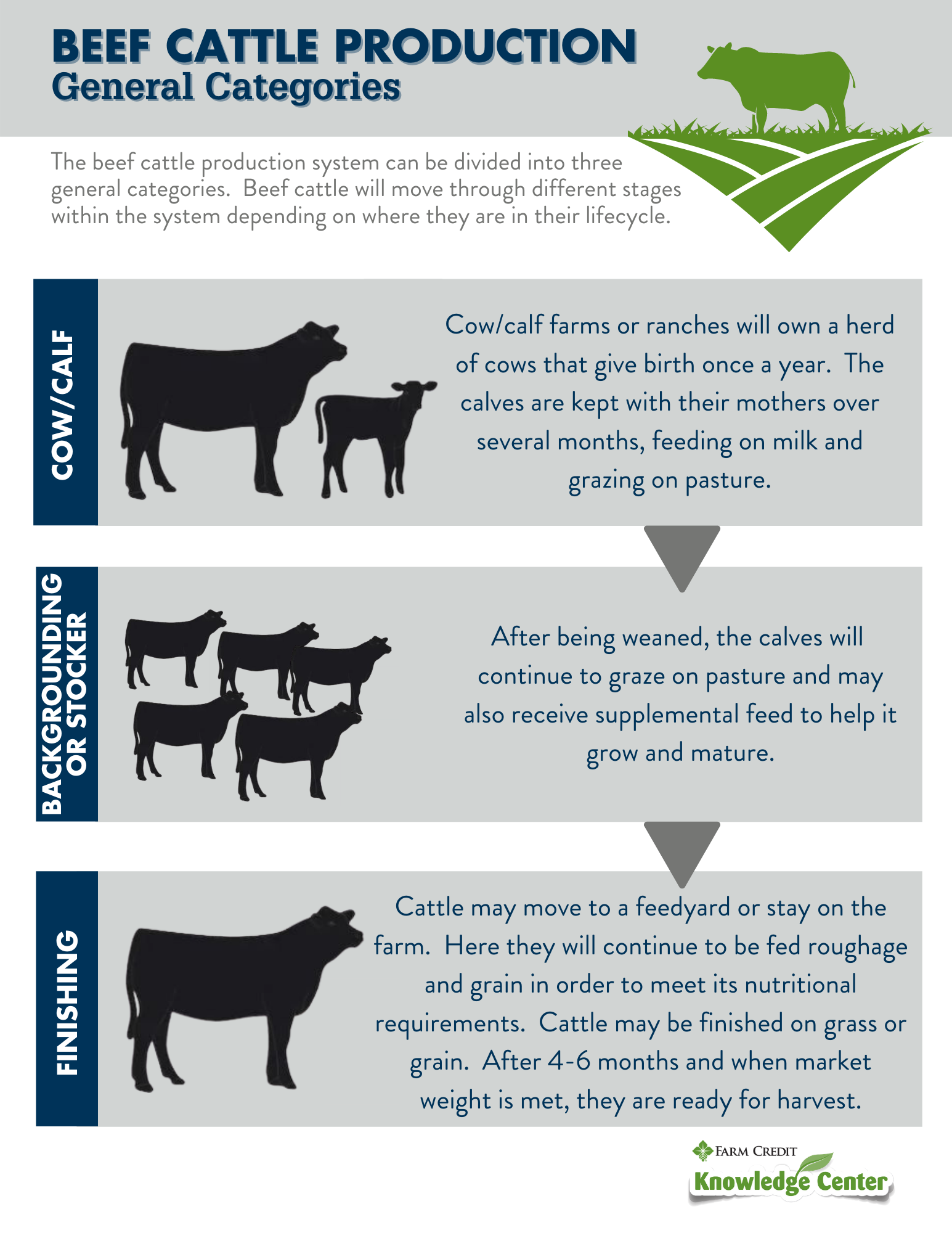
Stop by the Todays Agriculture display at the 2013 PA Farm Show January 5-12 at the PA Farm Show Complex Expo Center Harrisburg PA. To learn more abou. The beef cattle production system can be grouped into three categories.
However the lifecycle of beef cattle is a bit more expansive. Not all cattle are raised through the stages with the end goal of being market ready. Beef cattle are bred and raised to withhold different roles within the system to help maintain the industry.
Life Cycle of a Cow. Life cycle of a cow poster you have 2 options. Color and B W.
Print up the one you want to use onto white card stock. If you use the color poster print up and laminate. If you pick the B W color and laminate.
Hang up during your. Therefore the aim of this article was to apply the methodology of Life Cycle Costing LCC to beef production systems identifying production costs per functional unit and comparing them economically and environmentally from the integration of data about Life Cycle Assessment LCA. In this way the description of the evaluated systems and the methodology used for analysis are.
Sam animates his disgusting fantasies for hundreds of thousands of peopleCheck out my other channel Sam ONella Vloghttpswwwyoutube. Morphology Life Cycle and Pathogenesis. Taenia saginata is also known as the beef tapeworm.
It is found amongst beef eaters all over the world. The adult worm lives in the small intestine upper jejunum of human. This is the unarmed tapeworm of man causing taeniasis and it can cause cysticercosis in cattle.
Field To Fork. The Lifecycle Of Beef The Beginnings Of Beef. Beef begins when a cow gives birth on a Cow-Calf farm or ranch.
This breeding ground oversees. The pastoral setting of a ranch offers a calf its first glimpse at life along its mothers side. On a beef cattle farm the calves will stay with their moms until weaning around 4-6 months old.
On a cow-calf farm the calves are separated and then usually sold to a feedlot. We sell our cross-bred calves and our Angus bulls but keep our Angus heifers to grow the size of our herd. Id like to go through the typical lifecycle of beef cattle.
Well start with the brood cows. And we have brood cows here in the background along with their baby calves. These calves in the background are about six months old.
So well go back a few months when these cows calved. And well even go back another ten months from there and go back to when these cows were bred. We do use artificial.
A life-cycle assessment LCA model was developed to estimate the environmental impacts associated with four different US. Northern Great Plains NPG beef production systems. The LCA model followed a cradle-to-gate approach and incorporated all major unit.
A life cycle assessment LCA of the US beef value chain was conducted to develop baseline information on the environmental impacts of the industry including metrics of the cradle-to-farm gate feed production cow-calf and feedlot operations and post-farm gate packing case-ready retail restaurant and consumer segments. Life Cycle Assessments LCA are an increasingly popular method for accounting net GHG emissions across an entire beef production system such as from cradle-to-farm gate or cradle-to-consumption. In particular comparative LCAs that assess improved versus conventional beef management in nearby systems are useful for determining how much a given management shift might.
Heifer retention will decrease beef supply even more. That beef supply decrease will be short lived as the calves of these retained heifers move into the feedlot. Beef production should begin to increase again in 2004 or 2005 and will continue for three to.